Enhancing Team Performance in Hybrid-Flexible Course Learning: The Role of Team Communication and Atmosphere | The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning
Both effective communication and a balanced team atmosphere are critical for maximizing team performance in Hyflex courses. Educators should foster communication strategies that encourage open dialogue and critical thinking while maintaining a supportive team environment. Overemphasis on maintaining positivity may hinder constructive critique and diminish performance.
Assessment of Learner Engagement and Expert Evaluations of AI-Generated Versus Human-Created Interactive Content in an Online Course | The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning
This project seeks to investigate the impact of GenAI on the development and assessment of online course materials and learners’ engagement with these materials in the online learning environment. The study analyzed GenAI-generated multiple-choice questions, fill-in-the-blank exercises, and true-false activities during 3 weeks of a 14-week online course
Classroom Search Tool | Calendar and Scheduling | University of Calgary
Welcome to the University of Calgary Classroom Search Tool! This tool is designed to help users visualize and locate learning spaces on the University of Calgary Main Campus. This tool offers detailed information about all general assignment rooms (centrally-scheduled rooms).
Google Antigravity
a full development IDE with integrated Google Gemini. Like Claude Code, from the future. Amazing.
any-llm - One interface to switch between LLM providers
any-llm is a library that offers a unified interface for multiple LLM providers, making it easy to adapt to changing needs, markets, or costs. Built with official SDKs, it lets you switch models and providers on demand whether you’re building agents or any LLM-powered app.
This looks SUUUUPER useful - build against an abstract API that then translates that to various LLMs and providers so you can easily switch from AWS to OpenAI to AI Foundry etc.
GitHub - mozilla-ai/llamafile: Distribute and run LLMs with a single file.
Distribute and run LLMs with a single file. Contribute to mozilla-ai/llamafile development by creating an account on GitHub.
And it seems to work well, too. Download an LLM and application all in one file. Slick.
New Tool Tracks Unauthorized AI Usage Across Organizations -- Campus Technology
DevOps platform provider JFrog is taking aim at a growing challenge for enterprises: users deploying AI tools without IT approval.
Selected text
These unsanctioned implementations, known as shadow AI, can expose organizations to compliance violations, data leakage, and supply chain vulnerabilities. JFrog's tool automatically discovers both homegrown AI models and third-party API integrations, giving security and compliance teams visibility into AI usage they may not know exists
Tracing the thoughts of a large language model \ Anthropic
Anthropic's latest interpretability research: a new microscope to understand Claude's internal mechanisms
Selected text
Language models like Claude aren't programmed directly by humans—instead, they‘re trained on large amounts of data. During that training process, they learn their own strategies to solve problems. These strategies are encoded in the billions of computations a model performs for every word it writes. They arrive inscrutable to us, the model’s developers. This means that we don’t understand how models do most of the things they do.
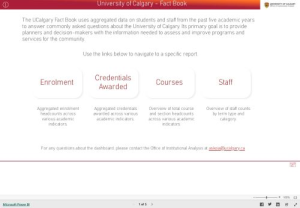
UCalgary Fact Book - OIA
PowerBI charts and tables for UCalgary data. Staff, students, etc.
Three Years from GPT-3 to Gemini 3 - by Ethan Mollick
From chatbots to agents
Selected text
Three years ago, we were impressed that a machine could write a poem about otters. Less than 1,000 days later, I am debating statistical methodology with an agent that built its own research environment. The era of the chatbot is turning into the era of the digital coworker. To be very clear, Gemini 3 isn’t perfect, and it still needs a manager who can guide and check it. But it suggests that “human in the loop” is evolving from “human who fixes AI mistakes” to “human who directs AI work.” And that may be the biggest change since the release of ChatGPT.
5 Creative Lecture Hall Installations That Optimize Space and ROI
Take your lecture hall installations to the next level while strategically staying within budget and space constraints with these 5 inspiring installation concepts.
A Month of Chat-Oriented Programming - CheckEagle
Against my expectation going in, I have changed my mind. I now believe chat-oriented programming (“CHOP”) can work today, if your tolerance for pain is high enough
-=:[ WarGames Terminal Fonts ]:=-
WarGames Terminal Fonts
Selected text
The font pack contains a total of nine operating system font files
-=:[ EPSON MX-80 Fonts ]:=-
EPSON MX-80 Fonts
Selected text
The EPSON MX-80 printer was a commercially successful product in the early
1980s. It was often used to print type in programs in computer magazines in
the 1980s. These fonts are therefore useful for retro printout simulation or
program listings on web pages and in documentation.
UAlberta non-credit micro-credentials guide
this is a great overview of their MC process, going beyond a simple framework. How can you implement a MC? etc.
Shifts and Transformations in Canadian Postsecondary Teaching and Learning: Views from Teaching and Learning Centre Leaders
Teaching and learning centres (TLCs) play a critical role in helping universities advance their strategic priorities related to teaching and learning. TLC leaders have a comprehensive lens that provides insights to help academic institutions move forward in addressing the shifts we are experiencing in postsecondary education. The purpose of this project was to conduct an environmental scan that broadly explores the shifts, transformations, and changes that TLCs are experiencing at Canada’s U15 institutions (large, leading research-intensive universities). We summarized these shifts, grounded key themes in scholarly research, and included recommendations to guide the work of TLCs and postsecondary institutions now and into the future. Teaching and learning centre leaders from U15 institutions (n=22) participated in semi-structured interviews over the fall and winter of 2024/25. Our themes surfaced from guiding questions that identified emerging and enduring shifts and transformations, the impact of these shifts, key priorities, and how to best strengthen postsecondary teaching and learning across institutions. Seven areas of focus for TLCs emerged, which are all grounded in and echoed by relevant academic literature: reflecting value; academic innovation and transformation; Indigenization, decolonization, and reconciliation; equity, diversity, inclusion, and accessibility; learning-focused; strategic priorities, planning, and resources; and, connecting, leadership, and well-being. These seven areas of focus informed our recommendations. TLCs play a critical role in addressing the challenges and changes affecting teaching and learning in post-secondary settings, now and into the future. There is a need for both academic transformation and relational transformation to address future priorities in higher education. TLCs should foreground strategic and relational academic leadership that commits to an ethos of compassion and care for those connected across the teaching and learning landscape. We hope this discussion paper will inspire dialogue amongst Canada’s postsecondary leaders, teaching and learning centres, and the broader academic community to enhance the work of TLCs and strengthen the quality of teaching and learning across institutions.
Assessment of Student Learning | Taylor Institute for Teaching and Learning | University of Calgary
Engaging with the UCalgary assessment principles
Selected text
The UCalgary Principles for the Assessment of Student Learning have been developed to support instructors as they design and implement of assessments based on their particular context and expertise.
Consultations have been underway at the governance level for these principles to be endorsed.
This page includes a brief description of links to relevant resources for each principle. The aim of these resources is to highlight current assessment practices and inspire future innovation
cancer trials Canada
Helping people living with cancer and healthcare professionals navigate cancer trial options
UCalgary Assessment Principles Report
The Assessment Principles Group (APG) was formed in 2023 to draft institutional Principles for the Assessment of Student Learning, based on input from across the University of Calgary (UCalgary).
Principles for the Assessment of Student Learning will provide a framework to help guide assessment practices, policies, guidelines, procedures, discussions, and decision-making across multiple organizational levels. Consultations with the UCalgary campus community began in the fall of 2024 and occurred over six months. Elder Evelyn Good Striker provided grounding, wisdom and guidance for our processes to help the team move forward in a good way. Over 450 people (staff, students and faculty) engaged in campus conversations, and nearly 900 comments emerged from and were coded from these consultations. Eleven themes emerged from this process including: student learning and growth; curriculum alignment; parallel processes and ethical space; equitable and inclusive; meaningful feedback; clear communication, mental health and wellbeing; academic integrity; educational technologies; continuous enhancement; and resources and support.
Matthew McConaughey and Michael Caine sign voice deal with AI company | Artificial intelligence (AI) | The Guardian
The voices of the Oscar-winning actors can now be used to create AI-generated versions in a new deal with ElevenLabs
I mean. Michael Caine is probably pretty much done doing voice acting. Maybe McConaughey's done after Salesforce and Lincoln and whatever? This doesn't seem like a great omen for all of the other actors trying to make a living doing this stuff.
Caffeinated Coffee Consumption or Abstinence to Reduce Atrial Fibrillation: The DECAF Randomized Clinical Trial | Atrial Fibrillation | JAMA | JAMA Network
Findings In this multicenter randomized clinical trial including 200 patients with persistent AF undergoing cardioversion, the risk of recurrent AF was significantly lower in the group allocated to coffee consumption (47%) compared with the abstinence group (64%).
Meaning Consumption of coffee and other caffeinated products may be reasonably considered in patients with AF.
Adopting AI across an institution is a pressing leadership challenge | Wonkhe
Janice Kay and Rachel Maxwell set out all the elements of a whole-institution AI strategy and the leadership capabilities required to make it real
Scrybble Sync - Think analog, organize digital
Seamlessly sync your reMarkable tablet notes with Obsidian. Transform handwritten insights into searchable, linkable knowledge. No more isolated notes.
Teaching and Learning Space Framework | Office of the Provost and Vice-Principal
Background The Queen’s University Teaching and Learning Space Framework (the Framework) is designed to shape the future design and renovations of centrally bookable teaching and learning environments. It also identifies methods for aligning class enrollment size and pedagogical approach with the most suitable learning space.
The future of campus classrooms | Queen's Gazette
Queen’s University has established itself as a leader in Canadian higher education when it comes to the creation of innovative classrooms that support dynamic styles of teaching and learning. It has invested in more than 20 spaces in recent years that promote the use of technology and active learning with features like movable chairs and multiple whiteboards or screens. Now it has adopted a strategic framework that builds on this success and will help ensure the campus has spaces that support the current and future needs of students and instructors.
Game design is simple, actually – Raph Koster
So, let’s just walk through the whole thing, end to end. Here’s a twelve-step program for understanding game design. One: Fun There are a lot of things people call “fun.” But most of them are not u…
GitHub - dlnorman/standalone-bookmarks
a lightweight, standalone, self-contained bookmarks management application intended for self-hosting on commodity web servers. - dlnorman/standalone-bookmarks
Build and Scale Applications - Generative AI Tools and Services - AWS
Learn about tools, implementation and how to get started building generative AI models with AWS.
Generative AI on AWS – Generative AI, LLMs, and Foundation Models – AWS
Discover the endless possibilities of generative AI on AWS to boost productivity, build differentiated experiences, and innovate.
Endless. Possibilities. Anyway, AWS does lots of AI stuff. Might be handy if we can get IT to finish spinning up an AWS environment to host SMARTIE et al.
How do I get started with the Team plan? | Claude Help Center
like it says on the tin.
Elders Cultural Transfers Video: Reg Crowshoe on Oral Systems
Part of the Elders' Wisdom Series. Reg Crowshoe shares teachings about oral systems.
How to implement AI Companion and train employees | Zoom
Zoom's AI Companion Onboarding resources
Get help introducing AI Companion to your organization with our collection of user guides, templates, best practices, demo videos, and more.
Going Deeper with Empathy Maps for Instructional Design
Empathy maps help learning designers see beyond surface-level traits to better grasp what motivates and challenges their audiences.
Selected text
Empathy maps bring learners’ perspectives into sharper focus, revealing insights that can transform how you design and create learning experiences
The Unsung Builders of Online Learning; IU Online
A centralized coordinating body, aligning and supporting online learning efforts across the Indiana University system
Selected text
IU Online serves as the central organization supporting online learning across Indiana University’s (IU) seven main campuses. Unlike many institutions that have expanded online by establishing separate campuses or new degree-granting entities, IU Online instead operates as a coordinating body, aligning and supporting online learning efforts across the Indiana University system. This isn’t a model often seen outside community college systems. A few university systems have attempted similar approaches, but Indiana is relatively rare in having made it work, and at scale.
A Strategic Plan Typology | HESA
Selected text
I have spent a few days recently reviewing new strategic plans at global top 200 universities (partly because of some talks I am giving in China and India this month, and partly because, as I mentioned yesterday, there’s a section on “what’s new in strategic plans” in our new World of Higher Education – Year in Review, out December 4th!). As a result of all this pondering, I think I have come up with a typology of sorts, which I thought I would share with y’all. Buckle up.
The format of strategic plans can, basically, be divided into three types.
SPACE TYPE GENERATOR
a cool text thing for making cool animated stuff with text. and gifs? slick.
AI Sandbox | Harvard University Information Technology
Explore generative AI in this secure environmentApproved to handle data classified as: Level 3
The AI Sandbox provides a secure environment in which to explore Generative AI, mitigating many security and privacy risks and ensuring the data entered will not be used to train any vendor large language models (LLMs). It offers a single interface that enables access to the latest LLMs from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Meta. Features include image generation, data visualization, and the ability to upload multiple files.
Compliance with University guidelines for use of generative AI required for use.
The Teaching Game: Strategic Course Design
a silly Claude-coded game based on my dissertation. maybe 2/3 playable? but maybe something interesting in there somewhere…
An Examination of Canadian Post-Secondary Faculty Beliefs Concerning Learning Strategies | The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
Instructors have opinions.
Even though faculty opinions were not in line with recognized evidence, their views provide insight into the learning strategies perceived as beneficial and those that students may be using
Enhanced Conceptual Learning with Real Time Student-Generated Data and Visualization | The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
Interactive student response systems (SRS, clickers) are used in post-secondary classrooms to enhance student engagement and learning. Their use, however, is most often limited to reviewing material with multiple choice questions. The present study examined student responses to a strategy for technology-enhanced learning within an introductory understanding research course to improve student experiences
Impacts of the Active Learning Classroom on Student Learning and Engagement: The Role of Technology | The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
Gah, with the forced acronyms.
This study examines student learning outcomes and engagement in a high-tech active learning environment compared to a low-tech active learning environment at both the individual lesson and overall course levels. A quasi-experimental design was employed, where two sections of students in a college Microeconomics course experienced a high-tech active learning classroom, while the other two sections engaged in the same activities in a low-tech classroom. Student perceptions of enjoyment were measured using the ENJOY scale, comprising five subscales: Pleasure, Relatedness, Competence, Challenge/Improvement, and Engagement
Turning crisis into opportunity: how entrepreneurs can thrive in turbulent times | News | University of Calgary
New study sets out to explore how AI can help minority-owned businesses turn disruption into innovation
HathiTrust Digital Library
apparently provides federated authentication for (post-secondary?) institutions across North America (or globally?)
The Fuzzy Front Ends: Reflections on the Never-Ending Story of Visualization Co-Design
Co-design is an increasingly popular approach in HCI and visualization, yet there is little guidance on how to effectively apply this method in visualization contexts. In this paper, we visually present our experience of a two-and-a-half-year co-design project with the local arts community. Focusing on facilitating community exploration and sense-making around arts funding distribution, the project involved a series of co-design sessions between visualization researchers and members of the arts community. Through these iterative sessions, we built shared understanding and developed visualization prototypes tailored to community needs. However, the practice is far from complete, and we found ourselves continually returning to the “fuzzy front end” of the co-design process. We share this ongoing story through comic-style visuals and reflect on three fuzzy front ends that we encountered during the project. By sharing these experiences with the visualization community, we hope to offer insights that others can draw on in their own community-engaged co-design work.
GenAI - Academic Integrity | University of Saskatchewan
The AI3 Model: Future Directions for Artificial Intelligence, Assessment Innovation, and Academic Integrity - Christopher DeLuca, Louis Volante, Michael Holden, 2025 BROKEN LINK
This article investigates this timely issue by examining the intersections between AI, academic integrity, and assessment innovations through a cross-national research synthesis, resulting in a novel model for educators, policymakers, and researchers. The proposed model promotes assessment policies and practices that support high integrity, authentic learning, and innovative student assessment in an era of generative AI.
We’re Losing the Thread on AI in Education
A call for systematic preparation in an increasingly reactive landscape
Selected text
Cognitive atrophy. An MIT study found that students who relied on ChatGPT to write essays showed diminished neural connectivity and couldn’t recall what they’d written minutes before. Eighty-three percent of AI users in the study couldn’t remember a single correct quote from essays they had just composed. The concern: we’re outsourcing thinking itself, and our brains are paying the price. Students might get correct answers, but they’re not developing the procedural fluency that enables genuine critical thought.
AI slop. Low-quality, AI-generated content now comprises half of all internet articles. Students wade through oceans of bland, generic, sometimes nonsensical material when they’re trying to research. UNESCO warns against AI’s tendency to produce “bland, generic, average, anodyne” content that crowds out more interesting perspectives. Teachers assign research projects, and students return with work that looks polished but is built on a foundation of algorithmically generated mediocrity.
Some Thoughts on the Use of AI in Teaching | HESA
I spent part of last week in Tempe at Arizona State University’s conference on Agentic AI and the Student Experience, which was a pretty interesting event. It made me think awhile about AI in higher education, which I thought I’d share with y’all. My POV on this basically comes down to six things: That last one […]
Selected text
Anyways, long story short: getting good at applying any new technology to pedagogy, AI or no, really comes down to time, resources, a willingness to experiment and a determination to share experiences and promote good practice at scale. The problem most universities have with technology adoption processes isn’t that institutions and/or faculty are anti-technology; it’s that modern universities make very little space available to talk pedagogy or to properly resource experimentation in pedagogy.